
TEL:+86 020-32166206/+86 020-32984581
Swipe left or right to see more categories
What are hazardous chemicals?
Time:
2023-07-05
Source:
Author:
What are hazardous chemicals?
Definition: Hazardous chemicals are highly toxic chemicals and other chemicals that are toxic, corrosive, explosive, flammable, combustible, etc., and are hazardous to humans, facilities, and the environment.
Classification of hazardous chemicals:
According to China's current published regulations, standards, there are three national standards: GB6944-86 "Classification of Dangerous Goods and Item No.", GB12268-90 "Dangerous Goods List", GB13690-92 "Classification of Commonly Used Hazardous Chemicals and Symbols", hazardous chemicals are divided into eight categories, each of which is divided into a number of items.
Category 1: explosives
Explosives refers to the role of the outside world (such as heat, friction, impact, etc.) can occur in a violent chemical reaction, instantly generating a large amount of gas and heat, so that the pressure around the sharp rise in the explosion, the surrounding environment, equipment, personnel damage and injury caused by the goods. Explosives in the national standard is divided into five items, three of which contain hazardous chemicals, the other two specifically refer to ammunition and so on.
Item 1: substances and articles with an overall explosion risk, such as perchloric acid.
Division 2: Dinitrobenzene, a substance with a higher risk of combustion than explosion.
Division 3: Substances and articles with a combination of a combustion hazard and a minor explosion hazard, e.g. dinitrobenzene.
Division 4: Substances and articles with no significant risk of explosion, e.g. tetrazolium-1-acetic acid.

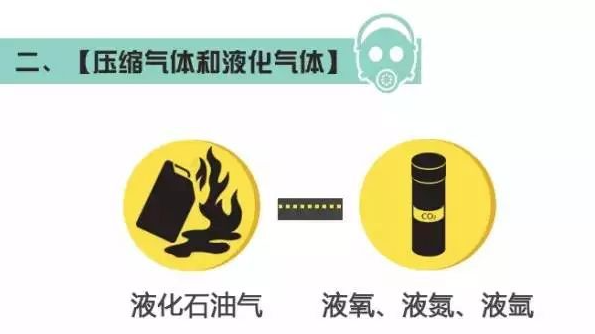
Category 2: Compressed and liquefied gases
Refers to gases that are compressed, liquefied or dissolved under pressure. When these items are subjected to heat, impact or strong vibration, the pressure inside the container increases sharply, resulting in rupture of the container, leakage of substances, explosion, etc. It is divided into 3 items.
Item 1: Flammable gases such as ammonia, carbon monoxide, methane, etc.
Item 2: non-flammable gases (including flammable gases), such as nitrogen, oxygen and so on.
Item 3: Toxic gases, such as chlorine (liquefied), ammonia (liquefied), etc.
Category 3: Flammable liquids
This category is volatile at room temperature and its vapour can form explosive mixtures when mixed with air. It is divided into 3 items.
Item 1: low flash point liquid, that is, the flash point of less than -18 ℃ liquid, such as acetaldehyde, acetone, etc..
Item 2: medium flash point liquid, that is, the flash point of -18 ℃ - < 23 ℃ of the liquid, such as benzene, methanol, etc..
Item 3: High flash point liquids, i.e. liquids with flash point above 23℃, such as cyclooctane, chlorobenzene, anisole, etc.

Category 4: Flammable solids, self-combustible articles and articles flammable in contact with moisture, which are prone to causing fires and are classified into three items according to their combustion characteristics.
Item 1: flammable solids, refers to the low ignition point, sensitive to heat, impact, friction, easy to be ignited by external sources of ignition, rapid combustion, can emit toxic fumes or toxic gases of the solid. Such as red phosphorus, sulphur, etc.
Item 2: Self-igniting articles, refers to articles with low spontaneous ignition point, easy to oxidise in the air and release heat, and burn themselves. Such as yellow phosphorus, titanium trichloride, etc.
Item 3: Wet flammable articles, refers to the water or moisture, a violent reaction occurs, release a large number of flammable gases and heat of the articles, some do not need an open flame, can be burned or exploded. Such as metallic sodium, potassium hydride, etc.
Category 5: oxidising agents and organic peroxides.
These items have strong oxidising properties, easy to cause combustion and explosion, according to its composition is divided into 2 items.
Item 1: oxidising agent, refers to substances with strong oxidising property, easy to decompose and release oxygen and heat, sensitive to heat, vibration and friction. Such as ammonium chlorate, potassium permanganate and so on.

Item 2: Organic peroxides, organic substances containing peroxide bonds in their molecular structure, which are inherently flammable and explosive, highly decomposable, and extremely sensitive to heat, vibration and friction. Such as benzoyl peroxide and methyl ethyl ketone peroxide.
Category 6: with drugs.

This kind of chemicals refers to the articles which can be accumulated to a certain amount after entering into the body, and can have biochemical or biophysical effects with body fluids and organs and tissues, disturbing or destroying the normal physiological functions of the body, causing temporary or persistent pathological changes in certain organs and systems, and even endangering the life. Oral ingestion LD50: solid LD50 ≤ 500mg/kg; liquid LD50 ≤ 2000mg/kg; skin contact for 24h, LD50 ≤ 1000mg/kg; dust, smoke and vapour inhalation LD50 ≤ 10mg/L of solid or liquid.
Category 7: Radioactive substances.
Refers to the human (animal) body, the accumulation of a certain amount of body fluids and tissues can be biochemical or biophysical effects, disturbing or destroying the normal physiological function of the body, causing temporary or persistent pathological changes, and even life-threatening items. Such as cyanide, arsenic, chemical pesticides and so on.
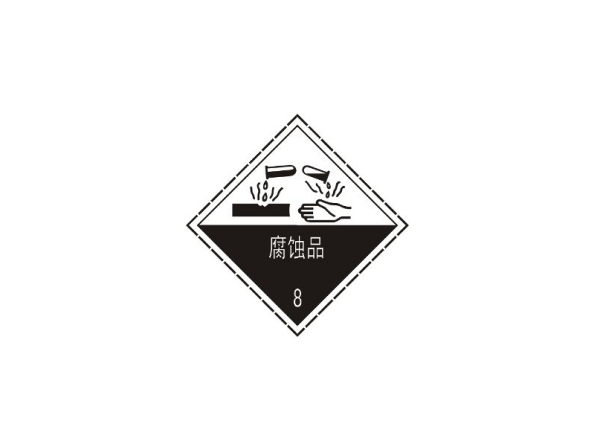
Category 8: corrosive products
Refers to the ability to burn human tissue and metal and other items causing damage to the solid or liquid. This kind of material according to the chemical nature of 3 items.
Item 1: Acidic corrosive products such as sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, etc.
Item 2: Alkaline corrosive products, such as sodium hydroxide, calcium sulphide, and so on.
Item 3: other corrosives, such as dichloroacetaldehyde, sodium phenol, etc.
Hazardous chemicals that are not included in the classification schedule may be classified by reference to articles of similar chemical nature and similar hazardous properties that are already listed.
2023-08-21
Bozhiyuan Technology (Guangdong) Co., LTD.
Add:5F, No.19, Rongjing Road, Hejing Yushan International, Zengcheng District, Guangzhou
Tel:+86 020-32166206
Mobile:+8613533086813
E-mail:S10@bzychemical.cn
